Infrared thermopile sensor working principle of the thermopile sensor
As long as any object is above absolute zero, it will radiate energy with a certain wavelength, but the radiation energy at low temperatures is fragile.
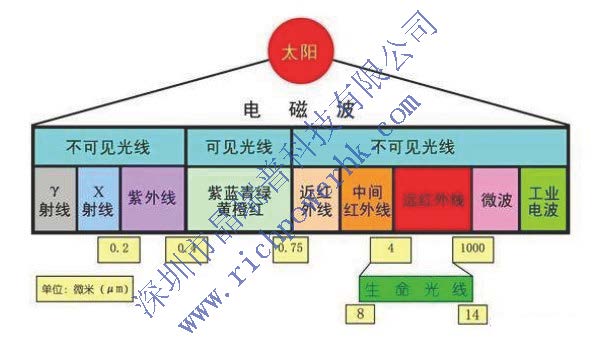
At room temperature, all objects in nature are the emission source of infrared radiation, but the wavelength of infrared radiation is different. For example, the infrared radiation wavelength of the human body at 37 ℃ is 9 ~ 10 μ m; the infrared radiation wavelength of objects at 400 ~ 700 ℃ is 3 ~ 5 μ M.
The non-contact temperature sensor is made of the principle that the object's radiation energy changes with the temperature.
The infrared thermopile sensor converts the infrared radiation absorbed into heat energy and converts the temperature change into an electronic signal amplified and displayed.
As a non-contact infrared temperature sensor, a thermopile can quickly measure the object's surface temperature without directly contacting the measured object. It can measure the high temperature, dangerous, or moving objects without polluting or damaging the measured object.
At present, it has been widely used in forehead temperature gun, ear temperature gun, intelligent home appliances, lamp switch, food temperature detection, and other fields.
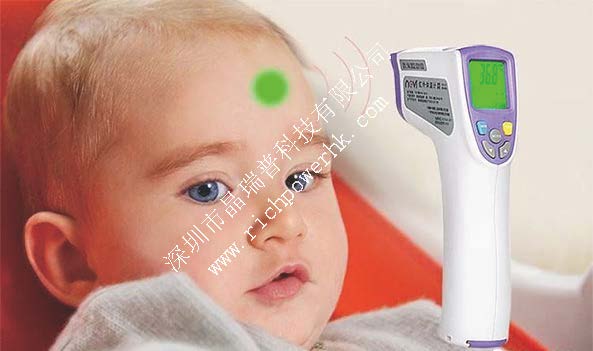

According to the Minamata Convention on mercury signed by the government representatives of the people's Republic of China in Kumamoto in 2013, since 2020, the production, import, and export of mercury-containing products are prohibited. Therefore, an electronic thermometer will replace the mercury thermometer and become the necessary forehead temperature gun and ear temperature gun for every household.
An electronic thermometer is a thermopile type infrared sensor that converts the infrared radiation of the human body into the change of the electrical signal to display the human body temperature. Compared with the traditional mercury thermometer, the electronic thermometer has the advantages of more safety, intuitive reading, short time, and high accuracy.
Thermopile is a closed-loop loop (i.e., a pair of thermocouples) based on the Seebeck effect mechanism. The higher temperature end of the two series connection is usually called "hot junction," and the lower end is called "cold junction." The carrier in the material moves along the direction of decreasing the temperature gradient, causing the charge to accumulate at the cold junction. There is thermoelectric power in the road.
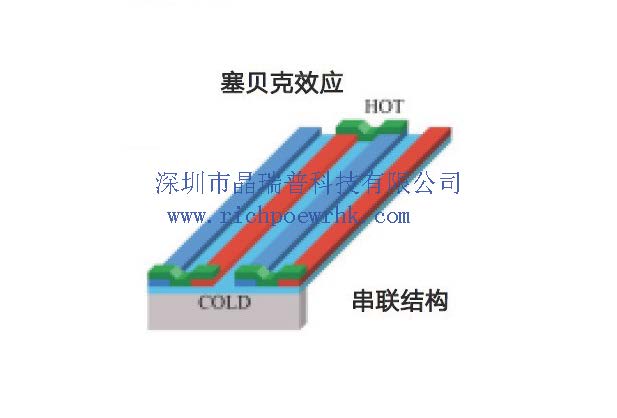
Thermopile is based on the seed effect mechanism, using silicon-based micromachining technology, arranging several thermocouples of thermopile on the support layer of the silicon chip, and connecting these thermocouples in series to form a thermopile chip. When the sensor receives infrared radiation, each thermocouple's voltage on the hot spot stack chip is superimposed and output; thus, the test temperature is transformed into a voltage signal

Physical drawing of hot spot reactor sensor (to-46 package)

The temperature sensor of the crystal gap thermopile
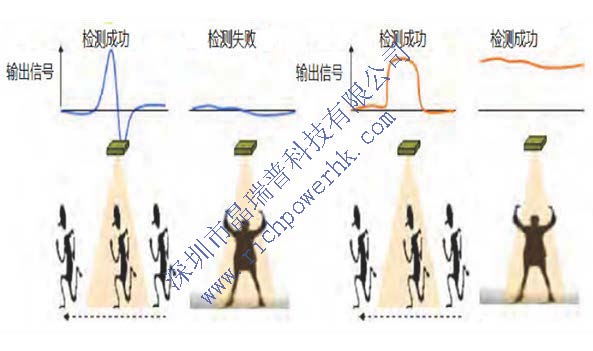
The difference between the thermopile sensor and the pyroelectric sensor can detect both dynamic and static signals and measure temperature accurately.
Picture of industrial temperature gun:




